Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Hajime; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sekine, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
In order to measure Fe-silicates precipitated under geological disposal conditions, a static leaching test has been conducted of simulated vitrified waste in 0.01 M FeCl solution with a surface area to volume ratio = 10 m
solution with a surface area to volume ratio = 10 m at 90
at 90 C under a N
C under a N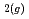 atmosphere. Obtained results indicate that Fe bearing minerals change from green rust to Fe-rich serpentine over time. Such mineral transitions are important as they may have an effect on the alteration behavior of glasses used for geological disposal of HLW.
atmosphere. Obtained results indicate that Fe bearing minerals change from green rust to Fe-rich serpentine over time. Such mineral transitions are important as they may have an effect on the alteration behavior of glasses used for geological disposal of HLW.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
High level radioactive vitrified materials are subject to monitoring during decades at storage facilities and over tens of thousands of years at final disposal sites. Although sufficient structural stability for long-term storage is necessary, high effluent filling which is often incompatible with mechanical and chemical integrity are required. The inhomogeneity of the glass yielded in preparation will cause the instability of the glass. Residual stress is one of the important parameters for evaluating the stability of the vitrified materials. Conventional stress measurement using a strain gauge reveal the averaged stress of whole specimen, however, local stress is also important because it can be an origin of the deformation or crack. Therefore, we developed a method using high-energy synchrotron X-ray stress measurements to clarify the local strain of the vitrified materials. Moreover, stress of each structural component such as crystalline and glass matrix can be separated by the method.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In order to establish vitrification technology, it is important to clarify how various substances dispersed in glass exist. We made simulated glass by mixing various substances containing metallic element of the platinum group with raw material glass containing SiO -B
-B O
O glass as the main component. This simulated glass was heated to 600
glass as the main component. This simulated glass was heated to 600 C just above the melting point and observed by an X-ray diffraction experiment. The obtained X-ray diffraction profile revealed the local structure using the pair distribution function (PDF). Since the network structure of SiO
C just above the melting point and observed by an X-ray diffraction experiment. The obtained X-ray diffraction profile revealed the local structure using the pair distribution function (PDF). Since the network structure of SiO is strong, it is considered that the precipitated fine particles become wedges and the Si-O bond length is modulated.
is strong, it is considered that the precipitated fine particles become wedges and the Si-O bond length is modulated.